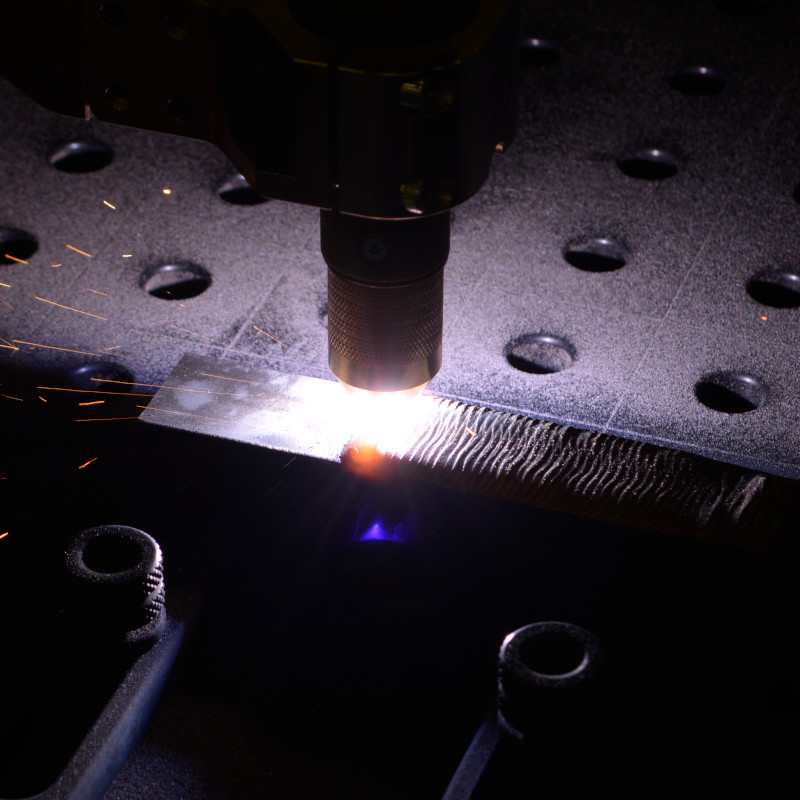
Plasma
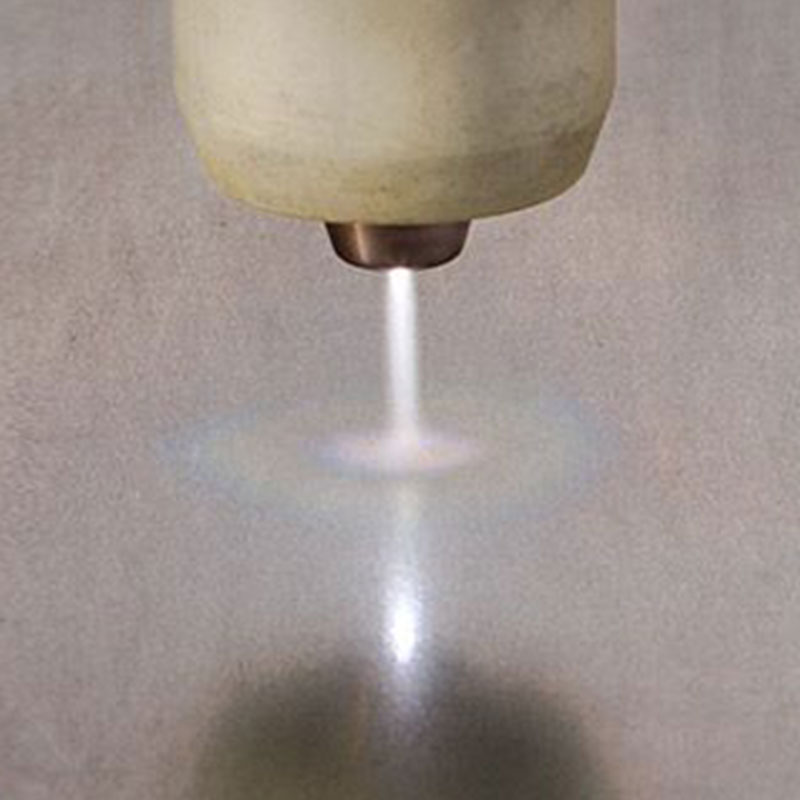
The plasma arc welding process is a suitable welding process for thin and thick sheet metals. In contrast to TIG welding, the arc in plasma arc welding is highly constricted via a cooled gas nozzle through which a plasma gas flow is routed. The arc focussed in this way delivers an excellent energy focus with deep penetration into the workpiece.
During ignition, a pilot arc is generated that burns with minimum current between the electrode and nozzle. This pilot arc is maintained in-between the welding processes, the number of RF ignitions is thus significantly reduced.
During plasma arc welding, higher welding speeds are achieved than during automated TIG welding.
Using the plasma method, thick sheets of up to 10 mm can be welded by means of the keyhole method. In this case, what is known as a keyhole is produced at the start of the weld. The molten metal flows and fills in the keyhole after the arc.
Advantages:
Pilot arc:
The pilot arc is established via HF ignition and does not have to be re-ignited for each welded part. This is particularly advantageous for EMC-sensitive areas.
Keyhole welding:
Plasma is particularly suitable for the keyhole method, where thick metal sheets can be welded efficiently with excellent results
Long wear part lifetime
Since the electrode in plasma arc welding is located on the inside in comparison to other welding processes, the lifetime of the wear parts are correspondingly high in comparison to other processes.
Welding speed
During plasma arc welding, higher welding speeds are achieved than during automated TIG welding.
Additional welding processes

Plasmatron

MIG / MAG
To the products
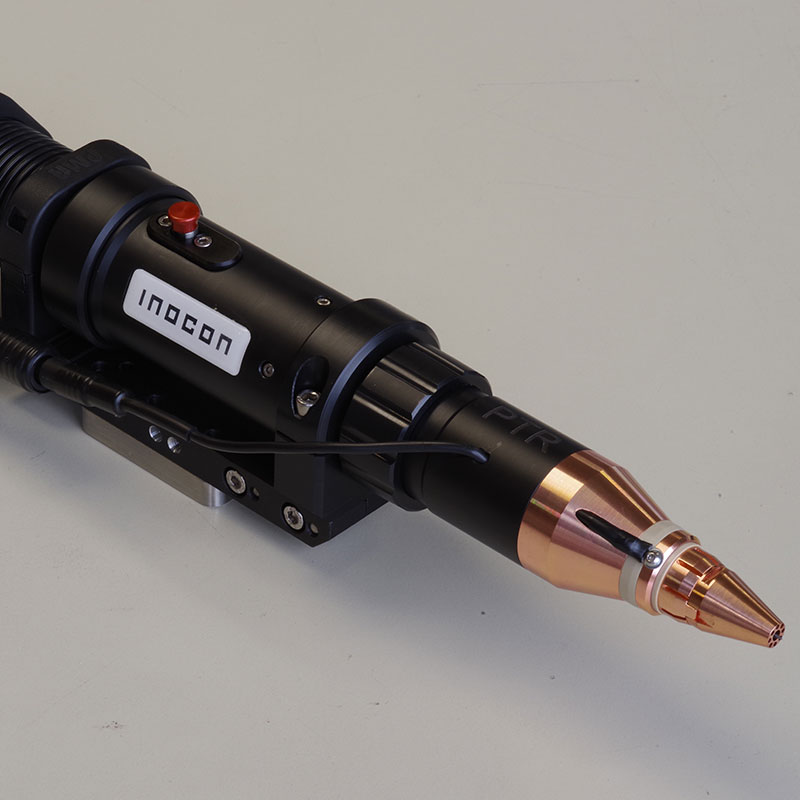

Plasmatron torch
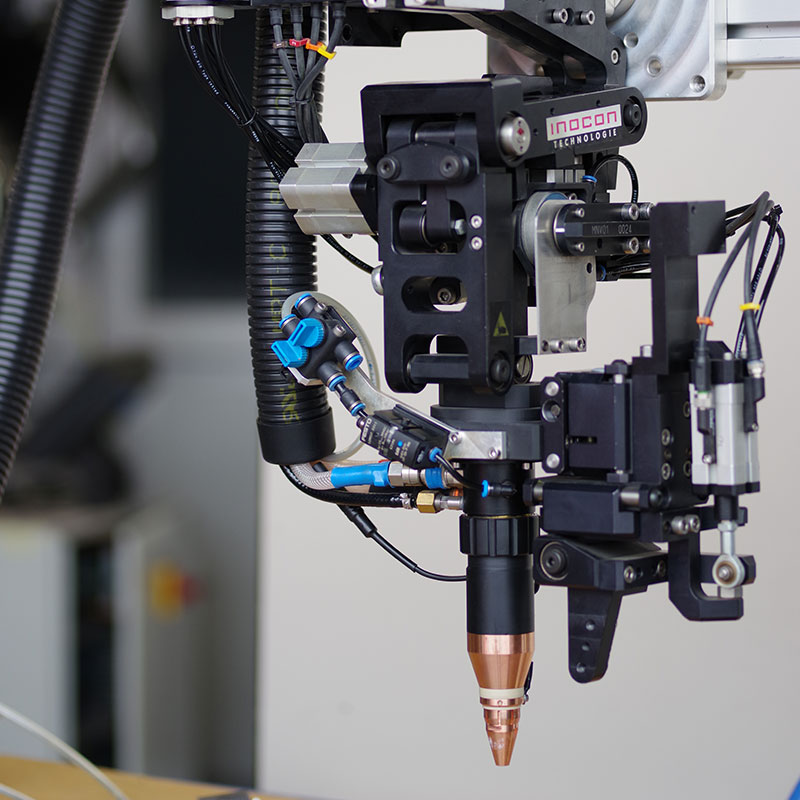
Seam guidance
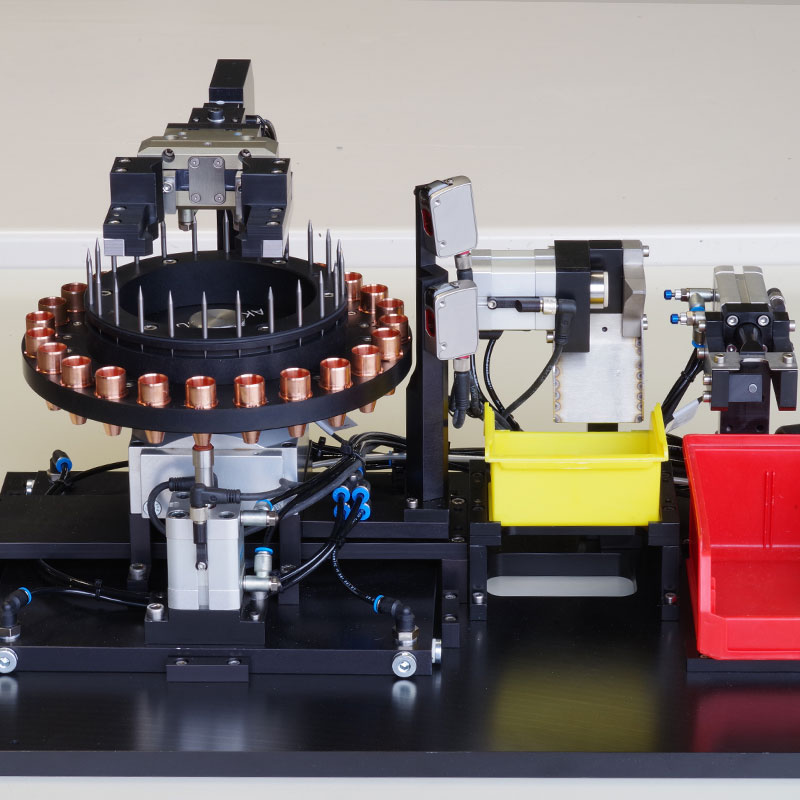
Cathode changer
To the projects
If this appeals to you, send us your application and become part of our team.